

Potential Source-Rocks
Foredeep Basin
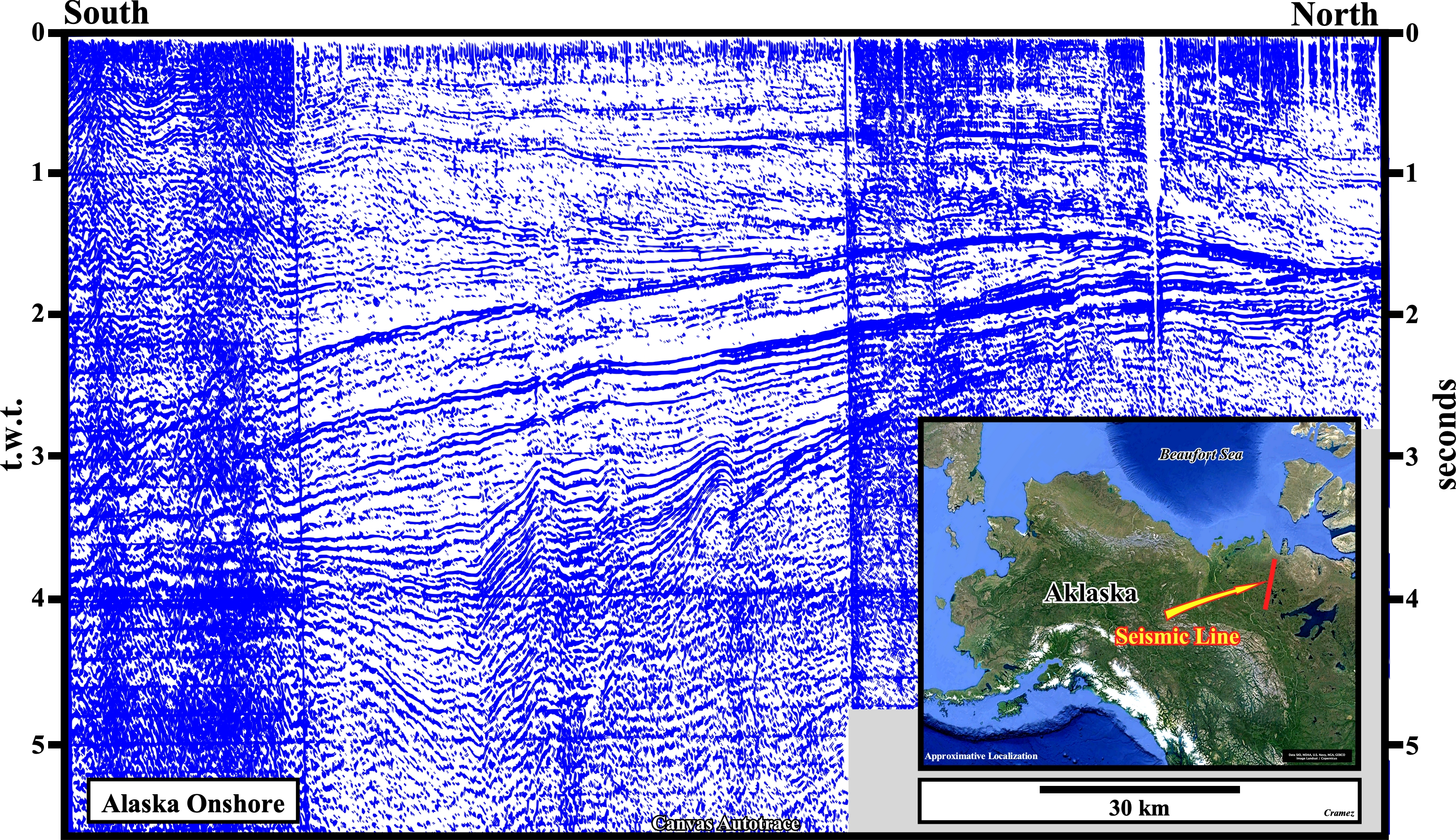
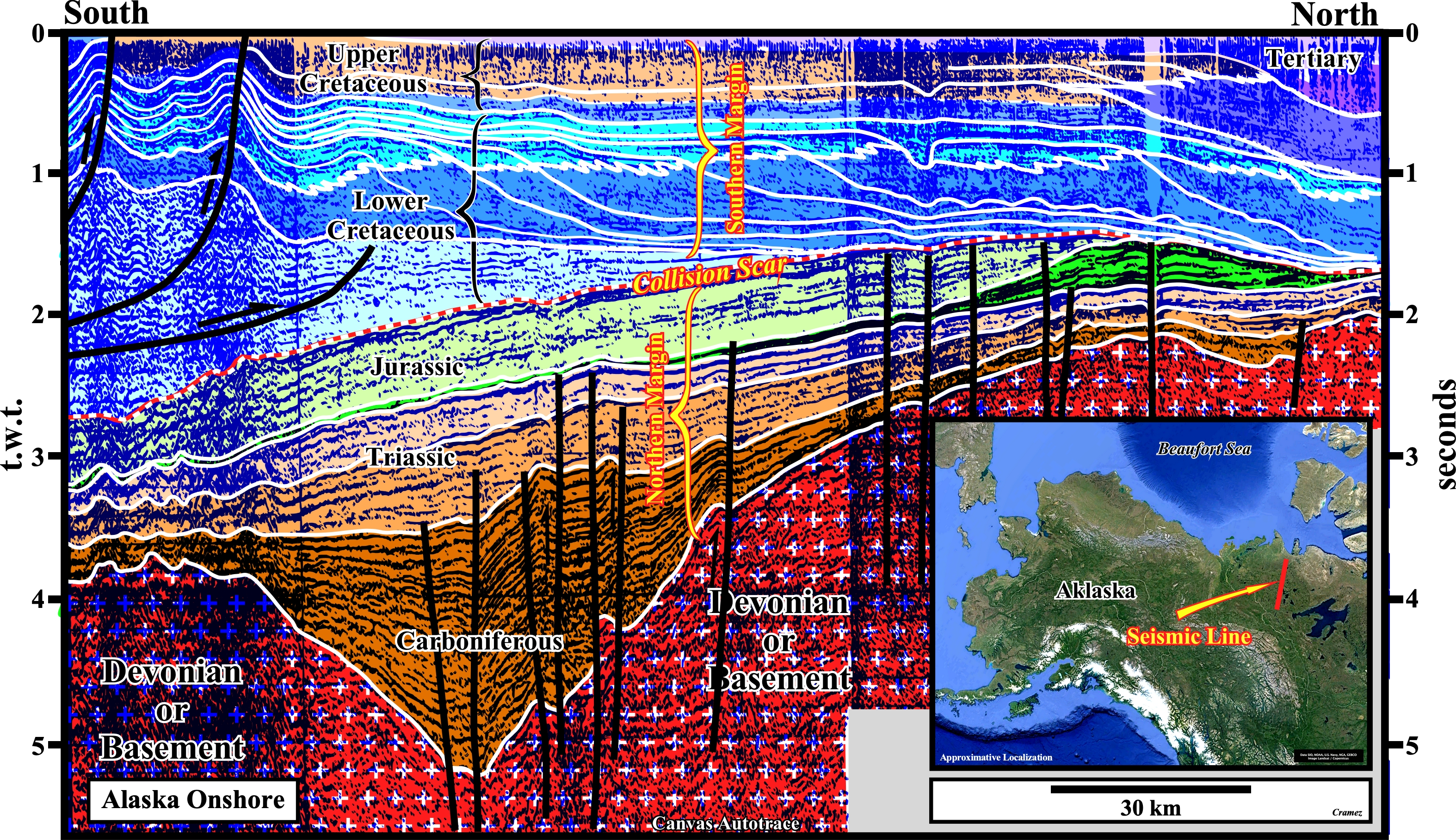
This Canvas autotrace from a regional seismic line from North Slope illustrates the Brooks fold belt (South), the Upper Cretaceous Collville foredeep basin (Middle) and the proximal section of the Tertiary Nuwuk Atlantic-type divergent margin (North). The fold belt is associated with a compressional tectonic regime, while the other basins are associated with extensional tectonic regimes. The foredeep basin was, mechanically, driven (by thrust loading), while the divergent margin was created mainly by thermal subsidence. The flexural bulge between the foredeep basin and the margin, i.e. the Borrow arch is, easily, recognized (see also next figure). The proposed interpretation underlies the closure of a pre-Pangea sea existent between the northern margin of a southern continent and the southern margin of a northern continent. The collision scan (red dotted line) bounds sediments prograding northward, which overlie sediments prograding seaward. The more likely generated petroleum sub-systems are associated with Lower Cretaceous and Jurassic downlap surfaces. The organic matter of both potential source-rocks seem mature, particularly, on the southern part of the this autotrace.
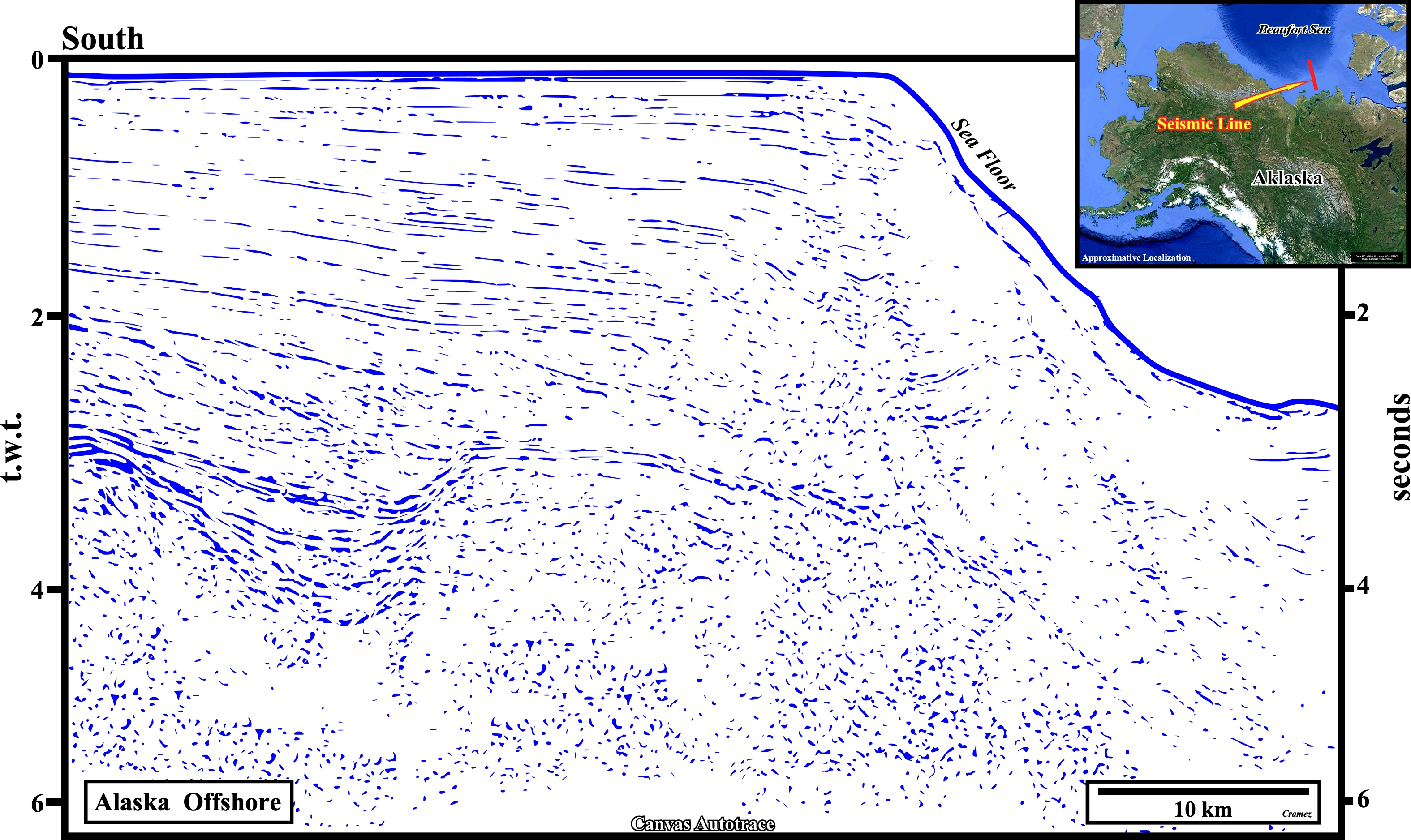
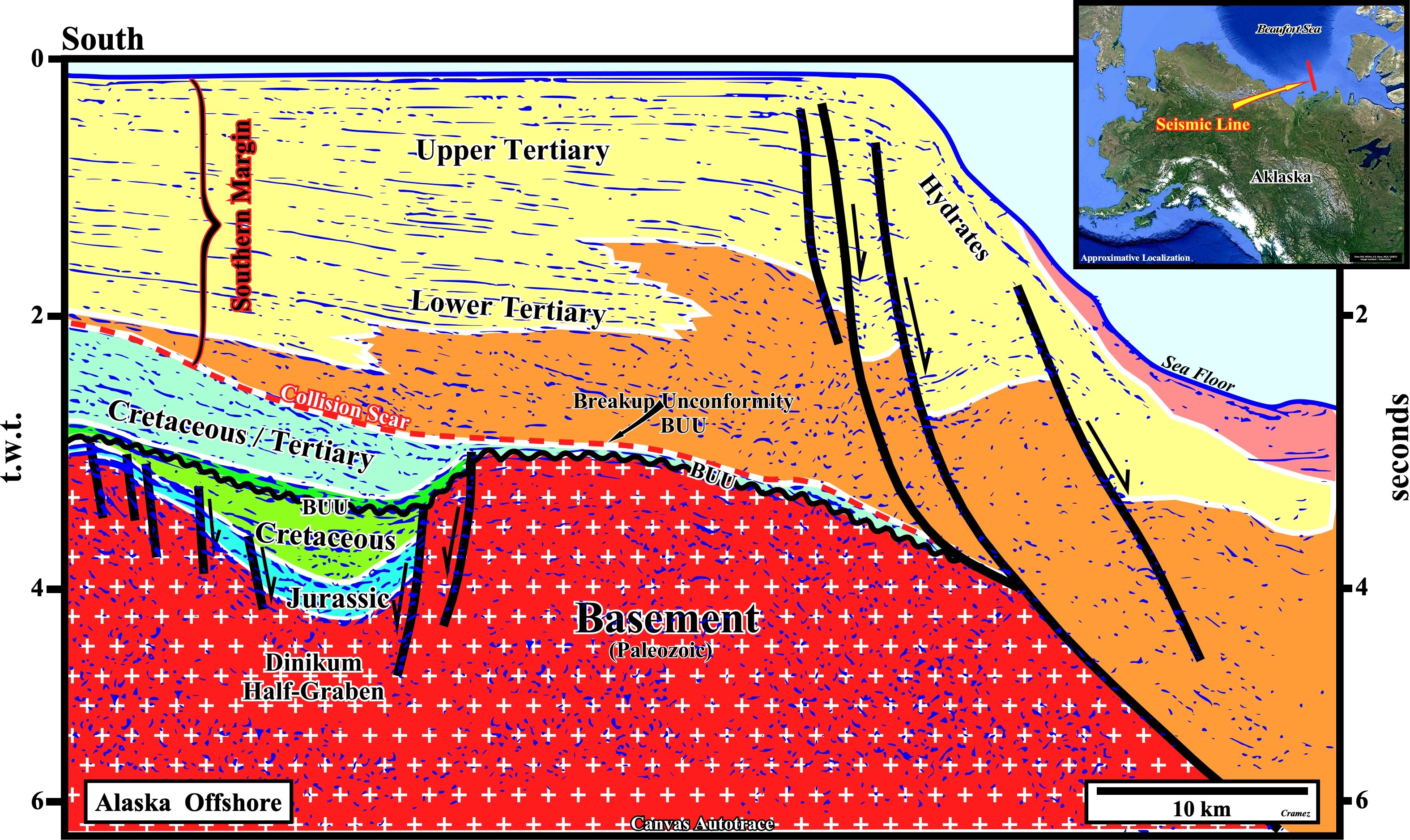
This Canvas autotrace is, more or less, the seaward continuation of the one illustrated on the previous autotrace. The tentative geological interpretation shows, mainly, the seaward shelf /slope transition of the southern divergent margin, i.e., above the collision scar (red-white dotted line). Obviously, the possibility of develop a generating petroleum sub-system in this margin, is quite modest. If there is a generating petroleum sub-system in the conventional offshore, it is most likely associated with the rift-type sediments (Jurassic-Lower Cretaceous), that is to say, in the sediments underlying the breakup unconformity (BUU) of the the northern margin (below the collision scar).
Send E-mails to carlos.cramez@bluewin.ch with comments and suggestions to improve this atlas.
Copyright © 2001 CCramez
Last update:
2022