

Vietnam Offshore
South Saigon Geographic Basin
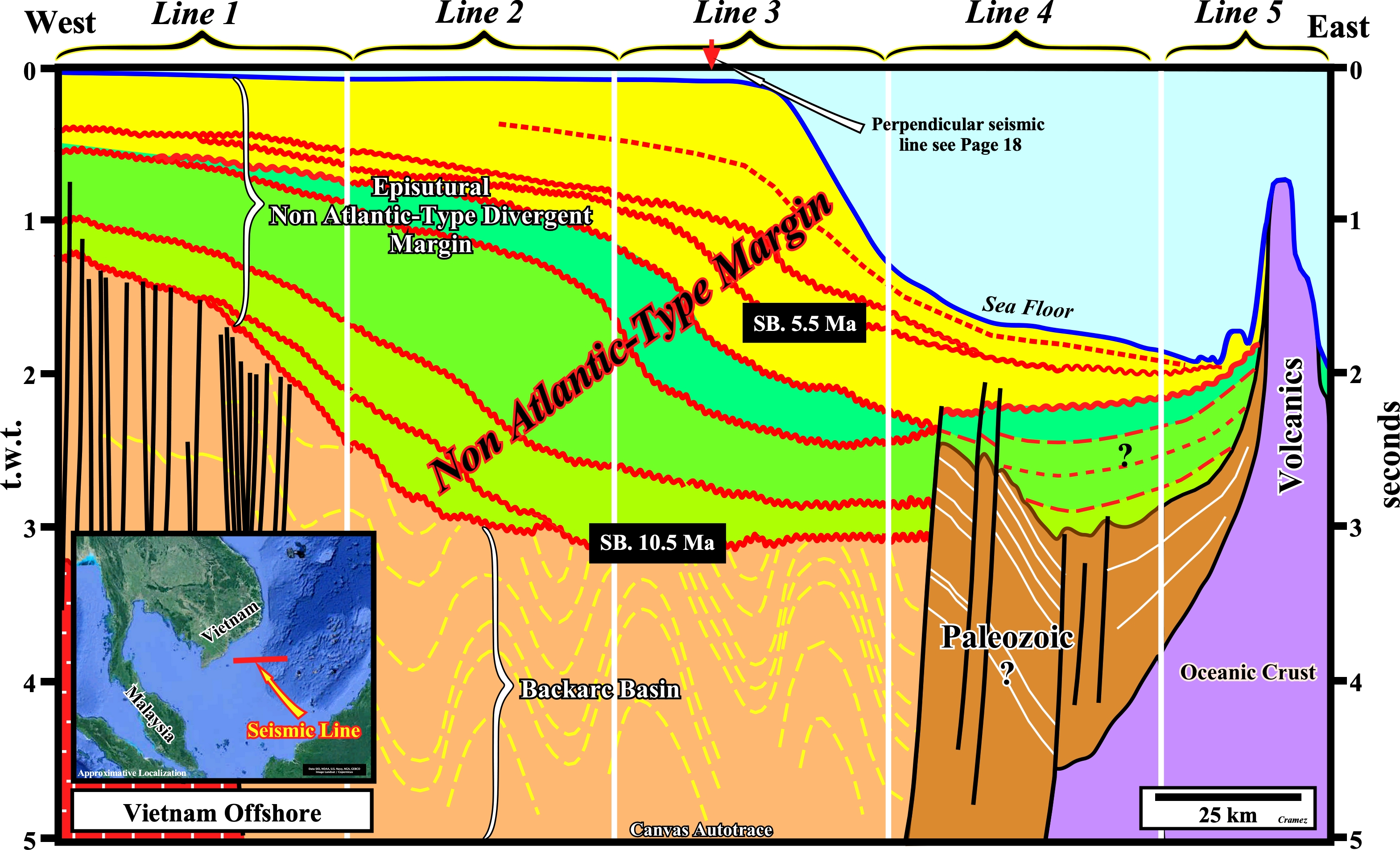
On this regional autotrace of a composite seismic line of the Vietnam offshore, a Paleozoic substratum is, easily, recognized, as well as, the oceanic crust and the volcanic plug, also called a volcanic neck or lava neck, i.e., a volcanic a body formed when the magma (molten or semi-molten natural material from which the volcanic rocks are formed) becomes solid within a fissure of an active volcano, of the right side of this tentative interpretation. Similarly, the deformed sediments of the backarc basin are, easily, recognized below the non Atlantic-type divergent margin, since the lengthening of the backarc basin induced an oceanization, i.e., the formation of new oceanic crust. Below, you can find Canvas autotraces and the respective tentative geological interpretations of the different seismic lines of the composite Canvas regional autotrace depicted above.
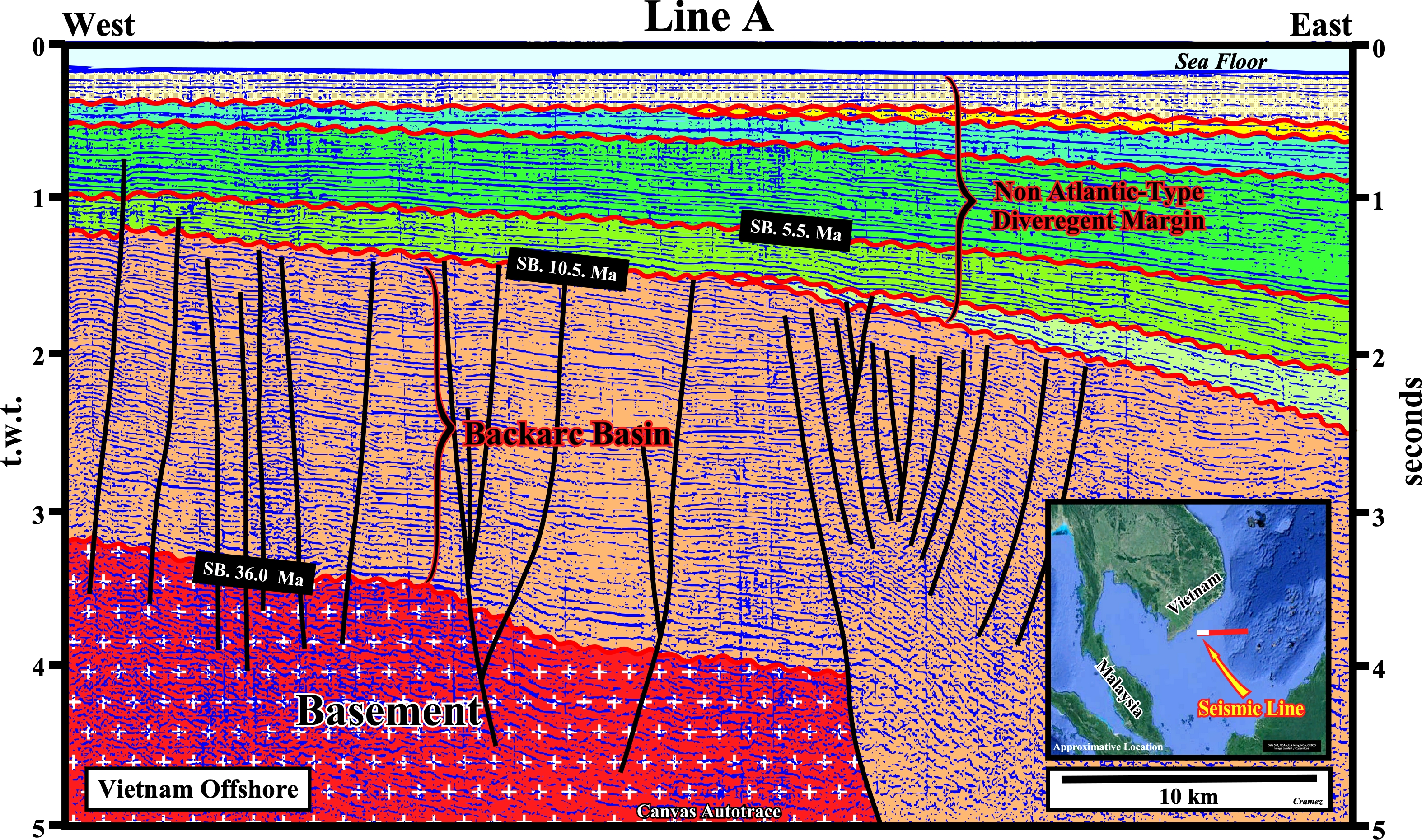
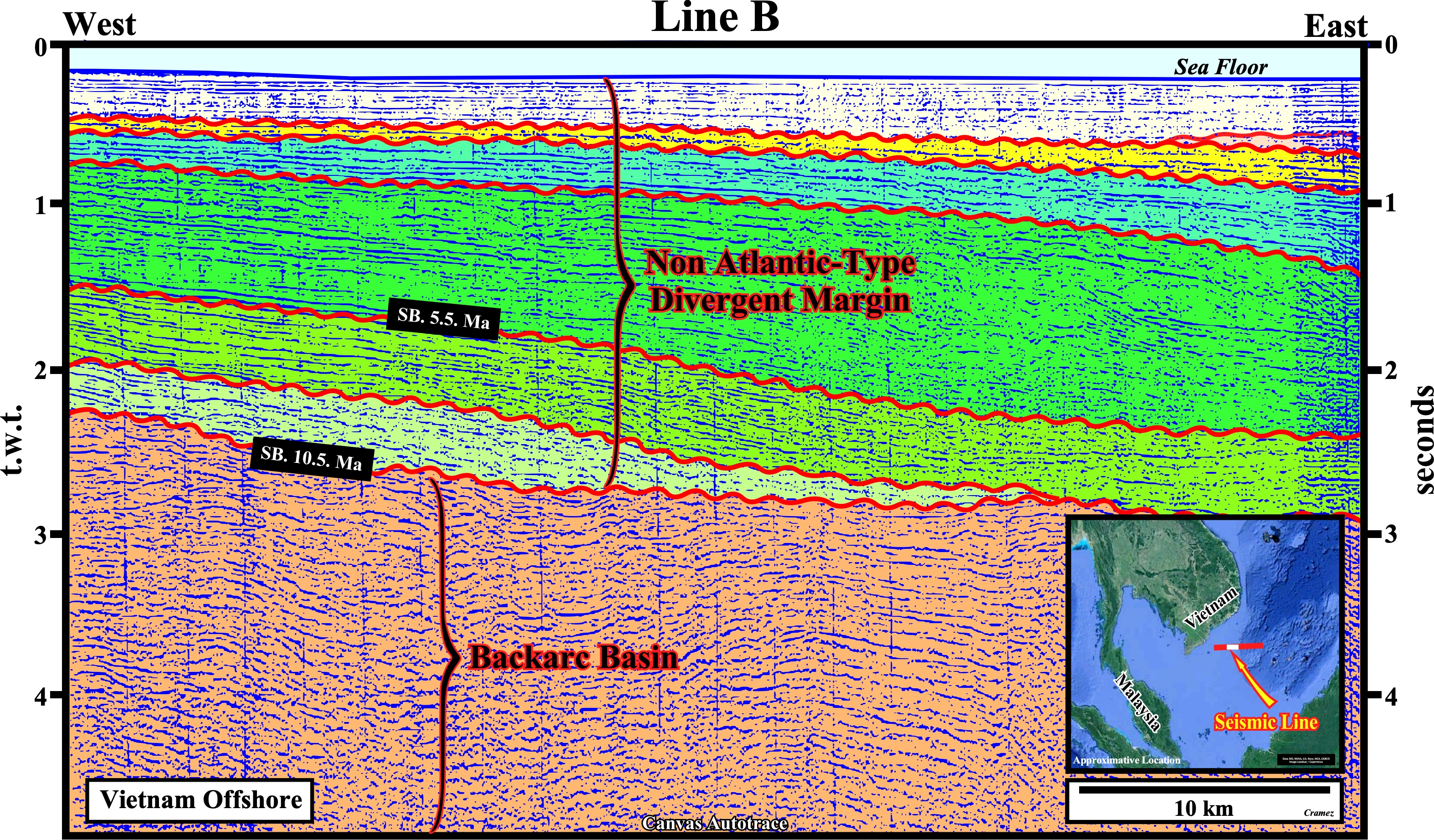
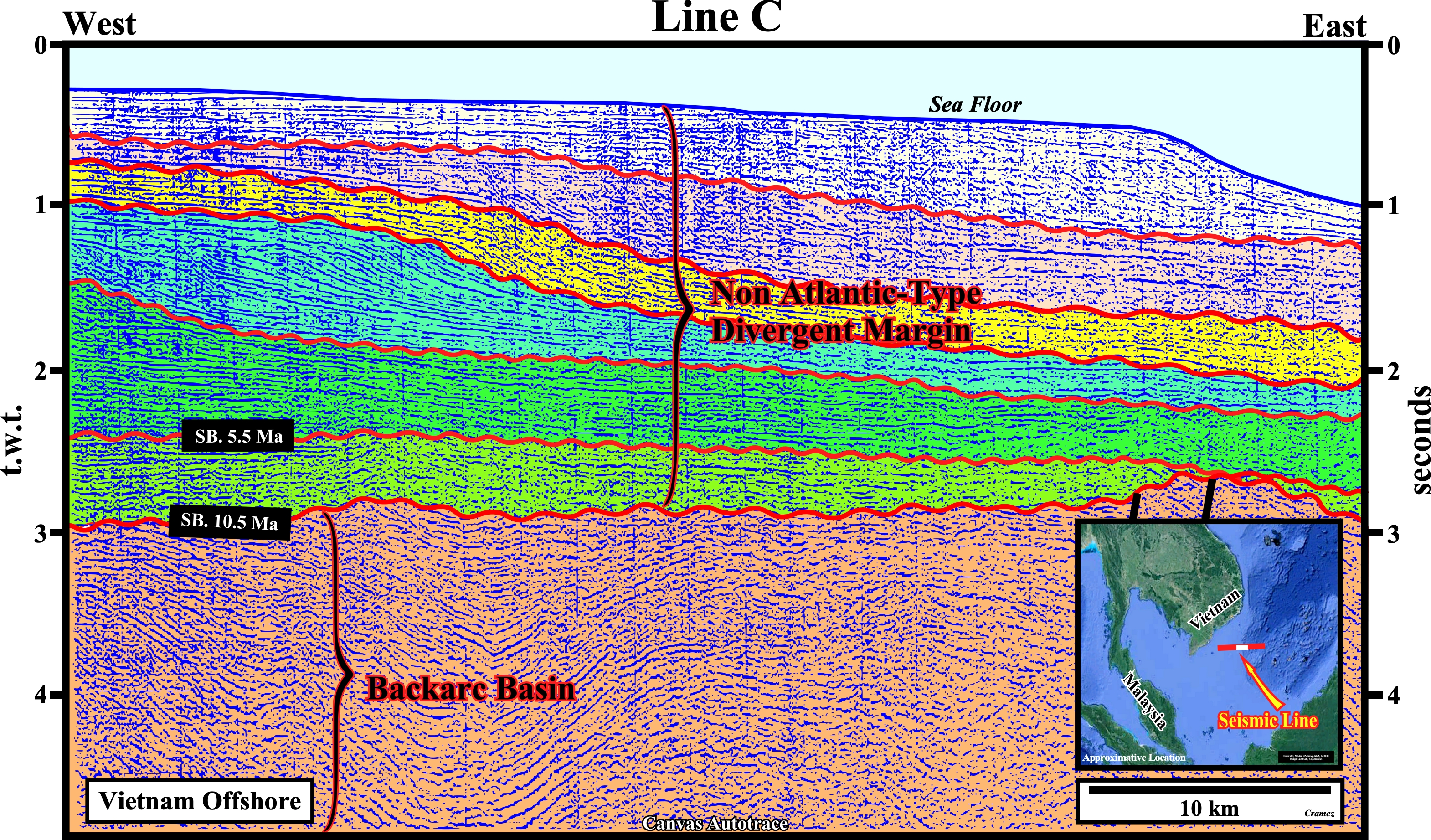
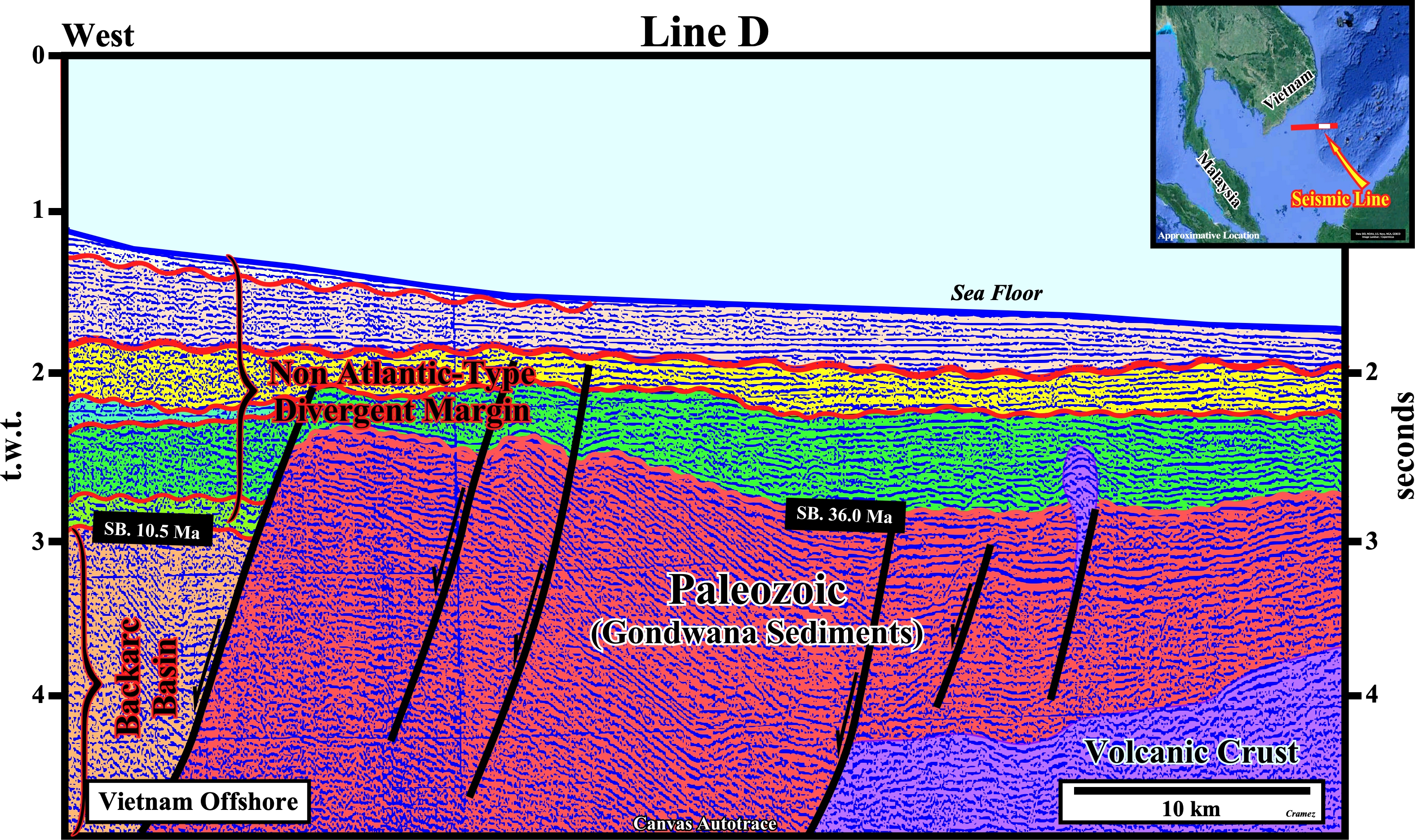
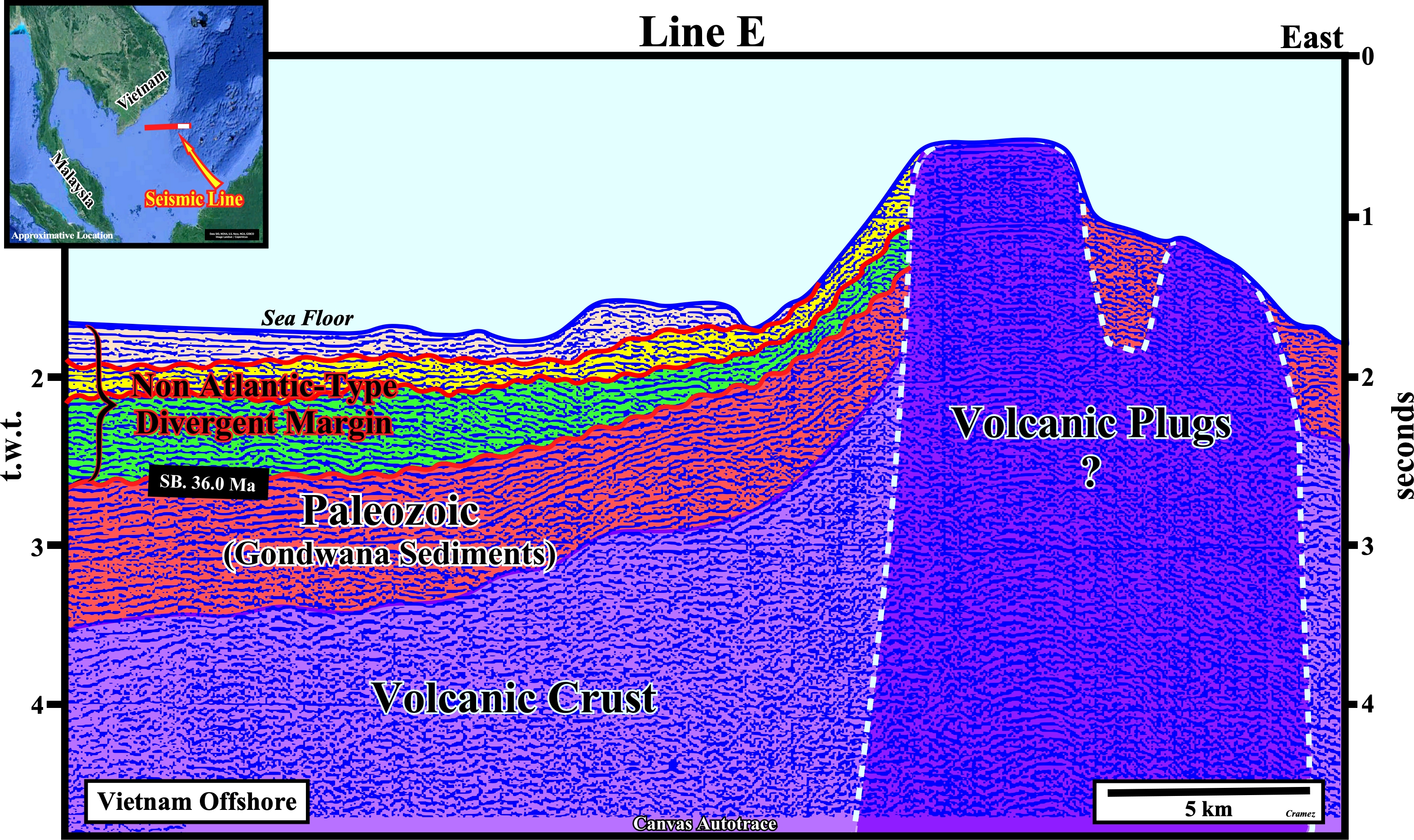
Take note that a non Atlantic divergent margin is formed during an oceanization (breakup of the continental crust with formation of new oceanic crust) in a global compressional geological context, i.e., within a megasuture, while an Atlantic-type divergent margin is formed, also, in association with the formation of new oceanic crust, but in an extensional geological context. The term megasuture was first used in 1975 by A. Bally to name an Earth's mobile region, i.e., folded and faulted mountain ranges, testifying the complexity of the accretion and deformation phases undergone by geological bodies in regions where compressional tectonic regimes predominate. Although the compressional tectonic regimes associated with the subduction zones are predominant in the formation of a megasuture, extensional regimes and the formation of sedimentary basins play, also, an important role. In the classification of the sedimentary basins, proposed by Bally, a non Atlantic-type divergent margins , developed in association with a B-type subduction zone, correspond, roughly, to a Mediterranean-type basin (developed in a A-type subduction zone), because there is oceanization, which is not the case in a Pannonian-type basin (see Page 21).
Send E-mails to carlos.cramez@bluewin.ch with comments and suggestions to improve this atlas.
Copyright © 2001 CCramez
Last update:
2022