

Indonesia Offshore
Ceram Trough
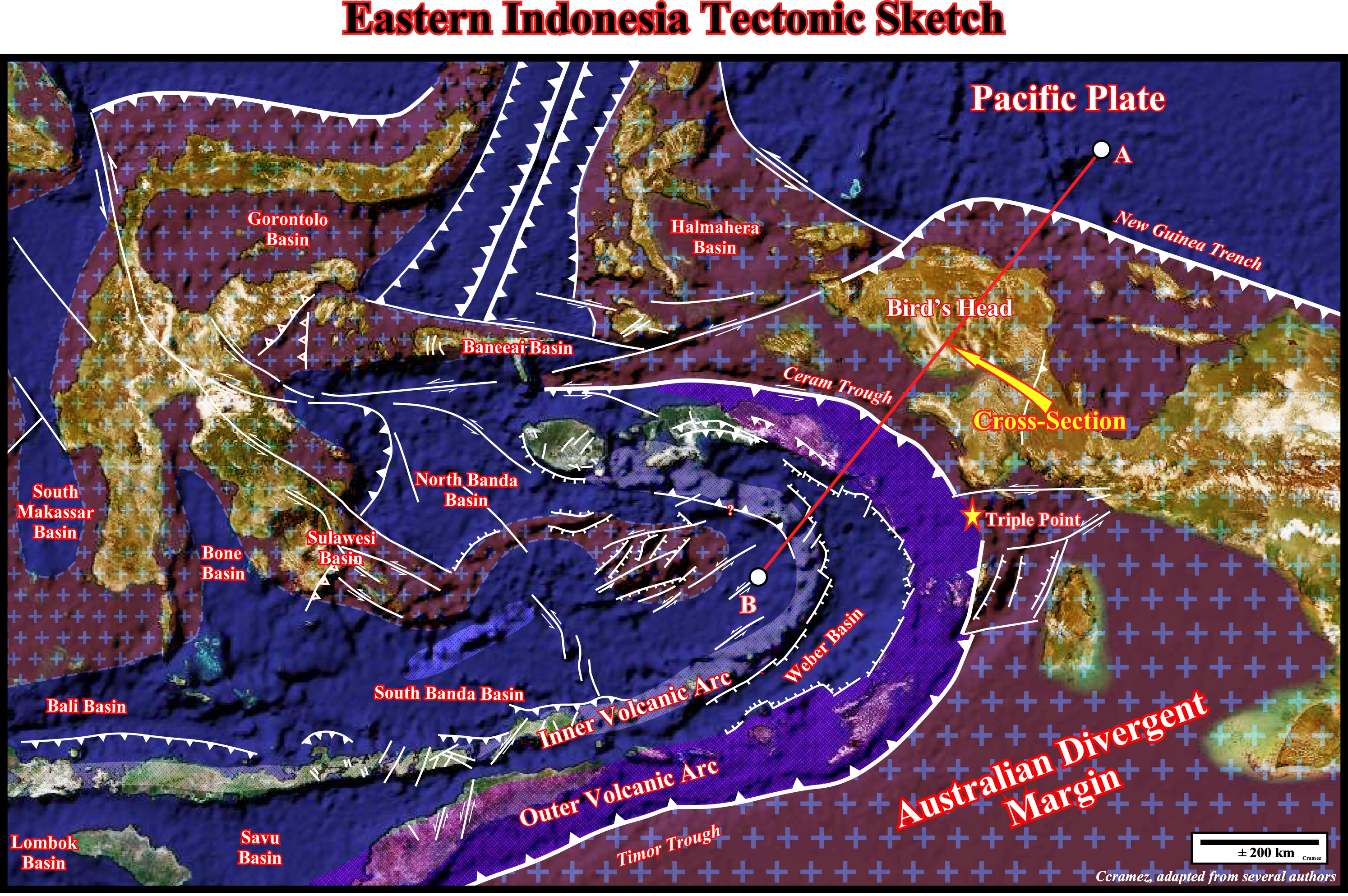
Taking into account this schematic tectonic sketch, it is quite easy to understand the Ceram trough between the Bird's Head platform and the Banda Sea plate. In fact, as said previously (Page 3A), the Ceram trough can be considered as the continuation of Timor trough with a small complication on the area of Kai Besar, where, as illustrated above, a micro-plate boundary, separated the Timor plate (in the southern area) from the Banda Sea plate, which contains part of Sulawesi Island, Ceram Island and Banda Islands. In plate tectonic terms, the A-B schematic geological cross section, illustrated on the next plate, summarizes the global geological setting of the area between the Banda Sea plate and the Pacific plate.
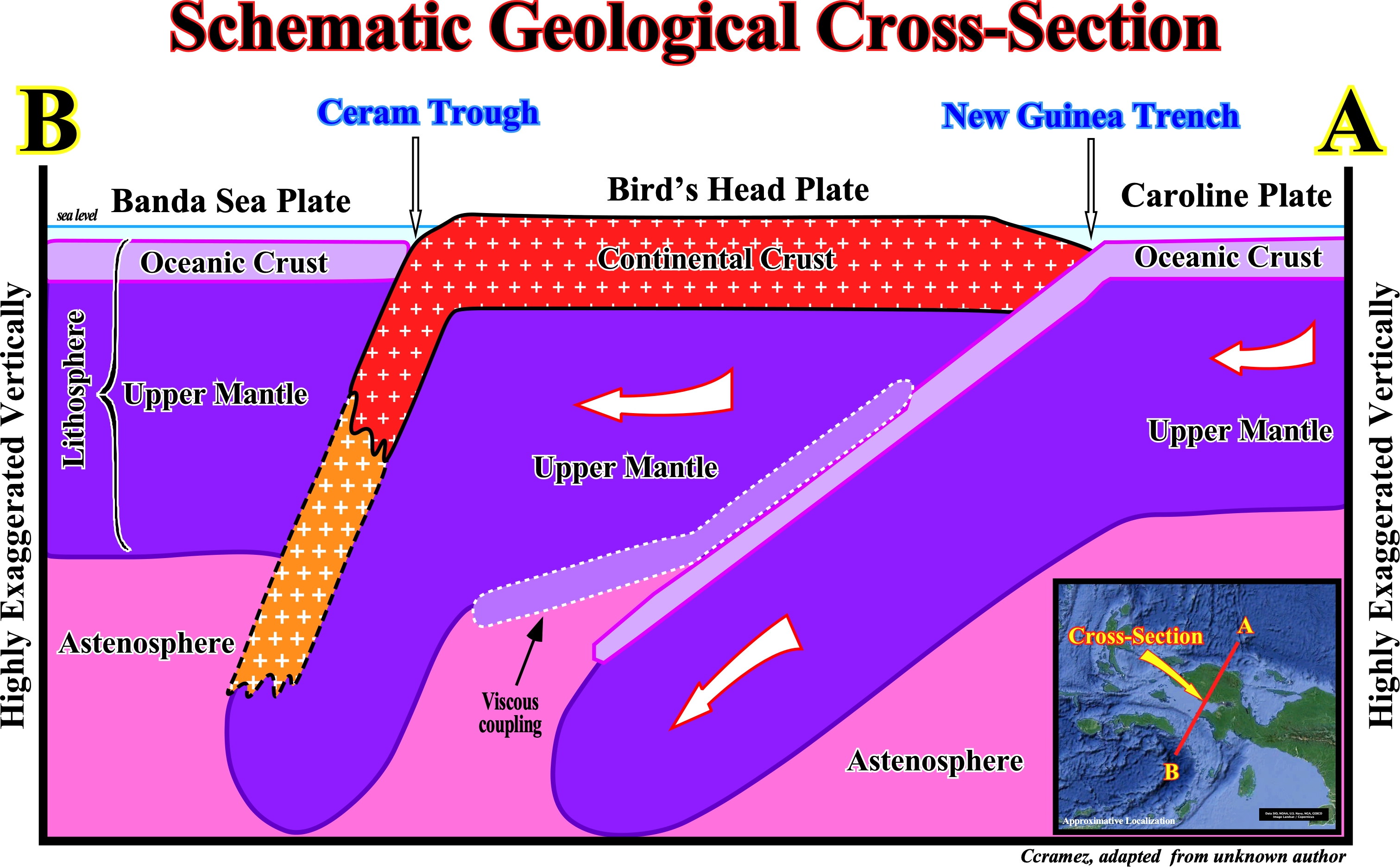
On this schematic geological cross-section with a quite high vertical exaggeration, three minor lithospheric plates are illustrated: (i) Banda Sea plate, which comprising, mainly, part the Banda Sea, Ceram Island, Banda Islands and part of Sulawesi Island ; (ii) Bird's Head plate composed by the Bird's Head Peninsula (western end of New Guinea), located NW from the Australian plate and the small Maoke plate and (iii) Caroline plate, considered part of the Pacific plate, which is subducting under Bird's Head and Woodlark plates in the south part of the New Guinea Trench. The Ceram trough, as well as, the New Guinea trough, is the consequence of the subduction of the Bird's Head plate (descending plate) under the overriding Banda Sea plate, on whch is an accretionary wedge is formed (see Page 28).

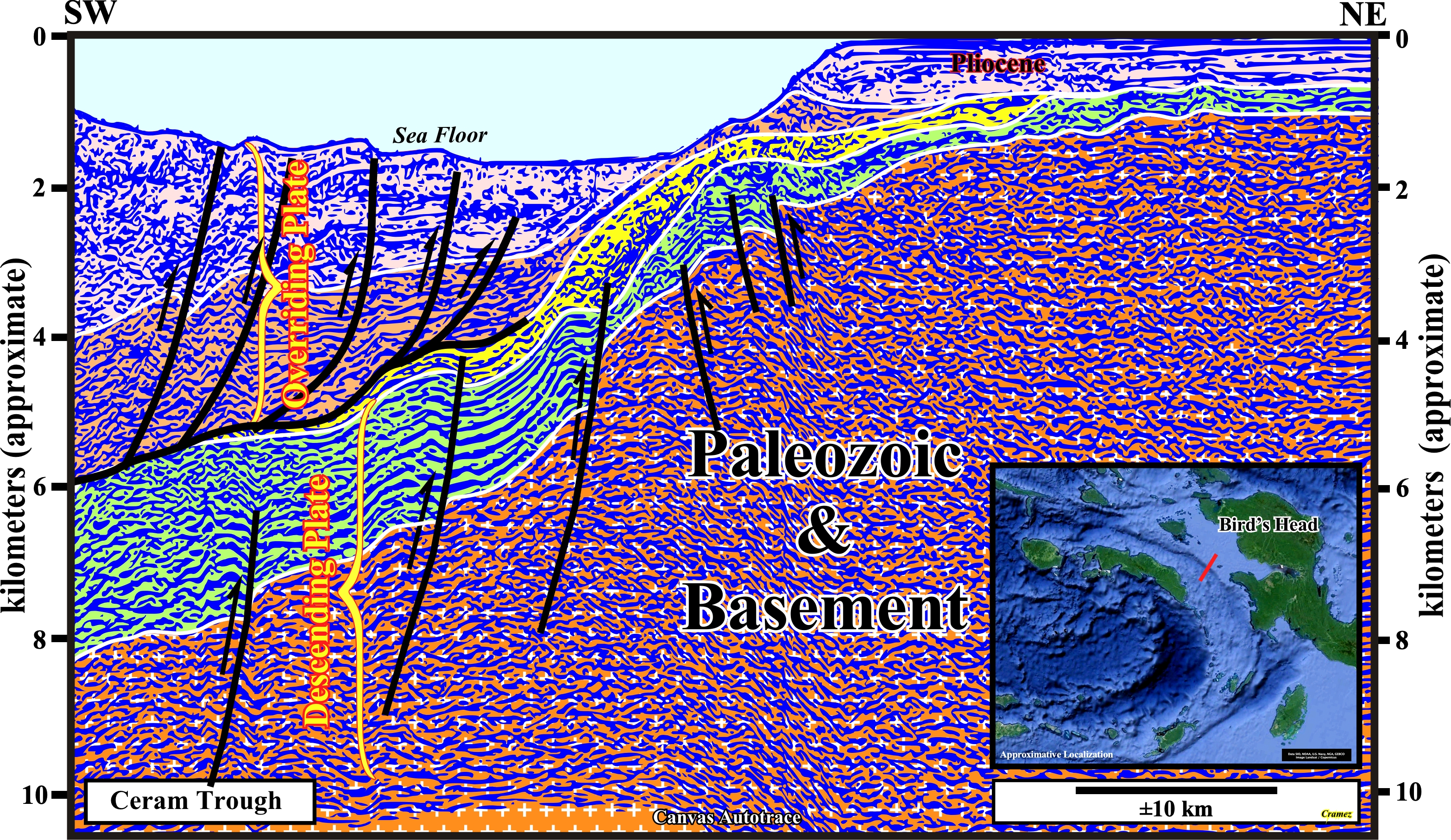
As illustrated on this autotrace of a seismic line between the Bird's Head and Ceram trough, the descending Australian lithospheric plate and the overriding plate, which corresponds to an accretionary wedge complex formed by an imbricated stacking Mesozoic to Miocene sediments, are recognized easily. Notice than the evolution of the north Ceram offshore is related to the separation of blocks at the northern Australian Atlantic-type divertgent margin, the extension and formation of the Tethys Sea and the collision of the Banda landmass with the Australian margin. Five stages are often considewred in such Ceram offshore evolution: (i) Initial riffing during the Early Triassic ; (ii) Late rifting, during the Middle Triassic-Middle Jurassic ; (iii) Breakup unconformity (probably during the Middle Jurassic) ; (iv) Deposition of an Atlantic-type divergent margin, during the Late Jurassic-Middle Miocene passive, and /(v) Thrusting during, the Late Miocene-Quaternary.
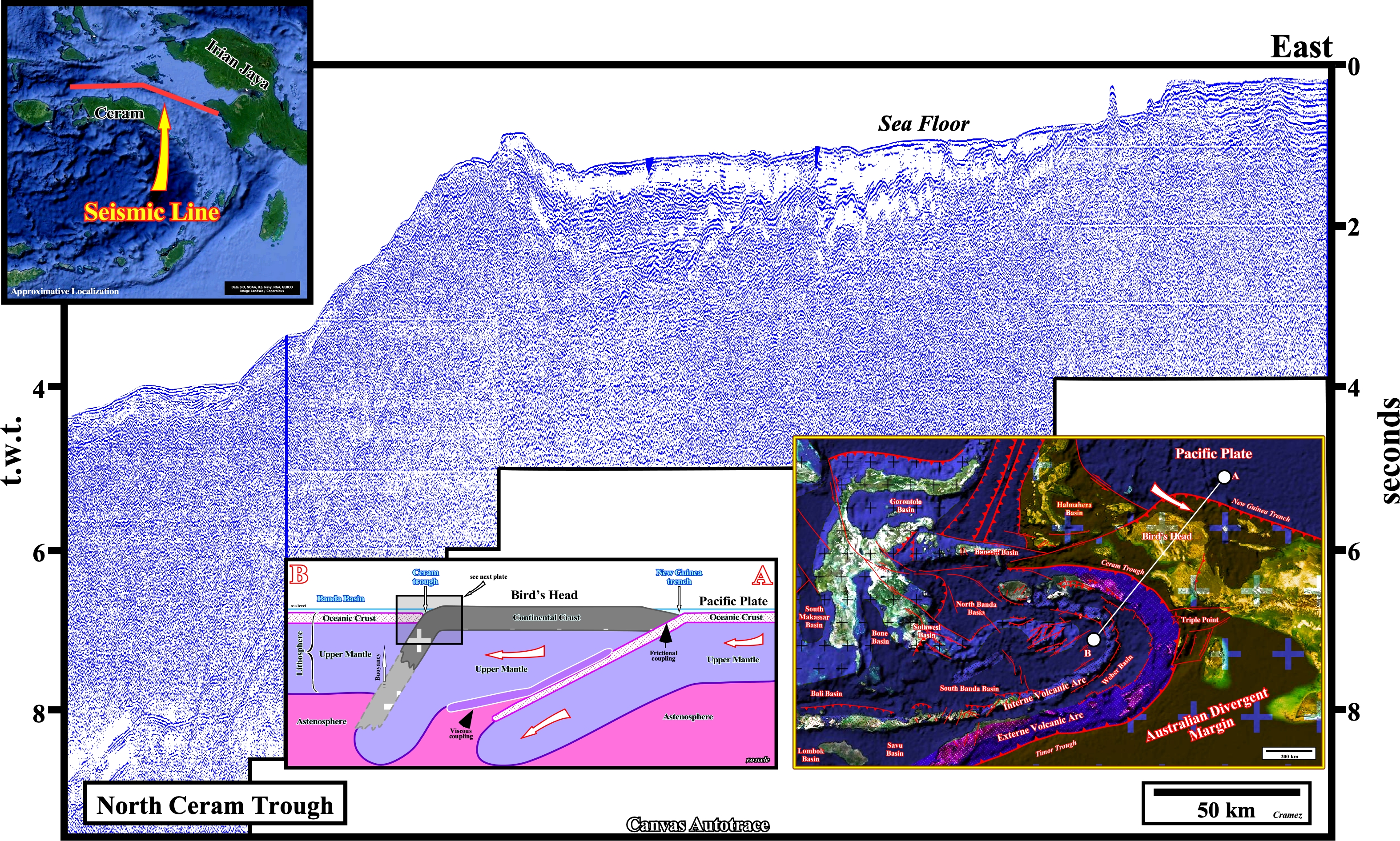
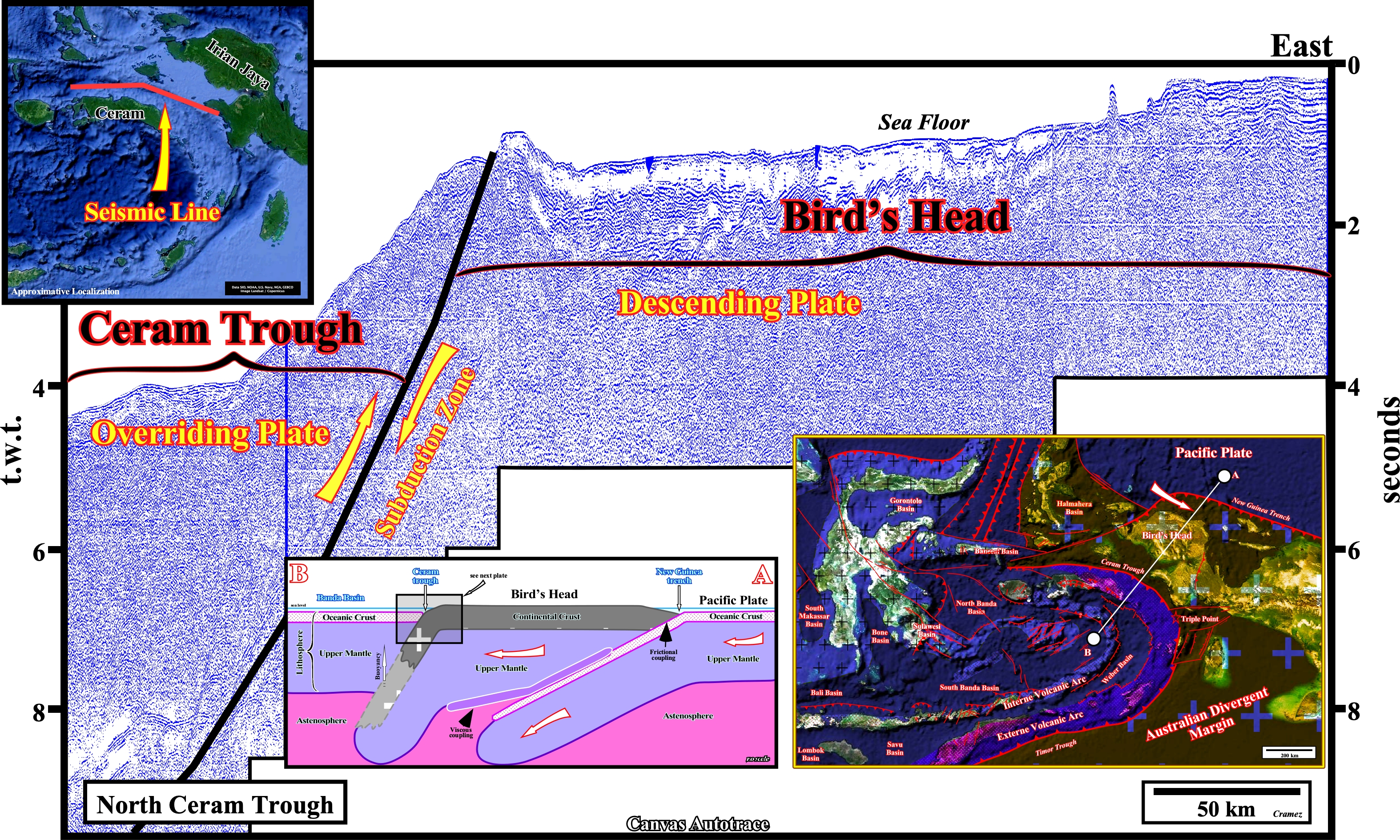
The limit between the Bird's Head (descending lithospheric plate) and the Ceram Trough (overriding lithospheric plate) is highlighted by a subduction zone, which isquite well marked on the bathymetry, taking into account thatthe composite seismic line is, mainly, a strike line.
Send E-mails to carlos.cramez@bluewin.ch with comments and suggestions to improve this atlas.
Copyright © 2001 CCramez
Last update:
2022