.jpg)
.jpg)
Tanzania Offshore
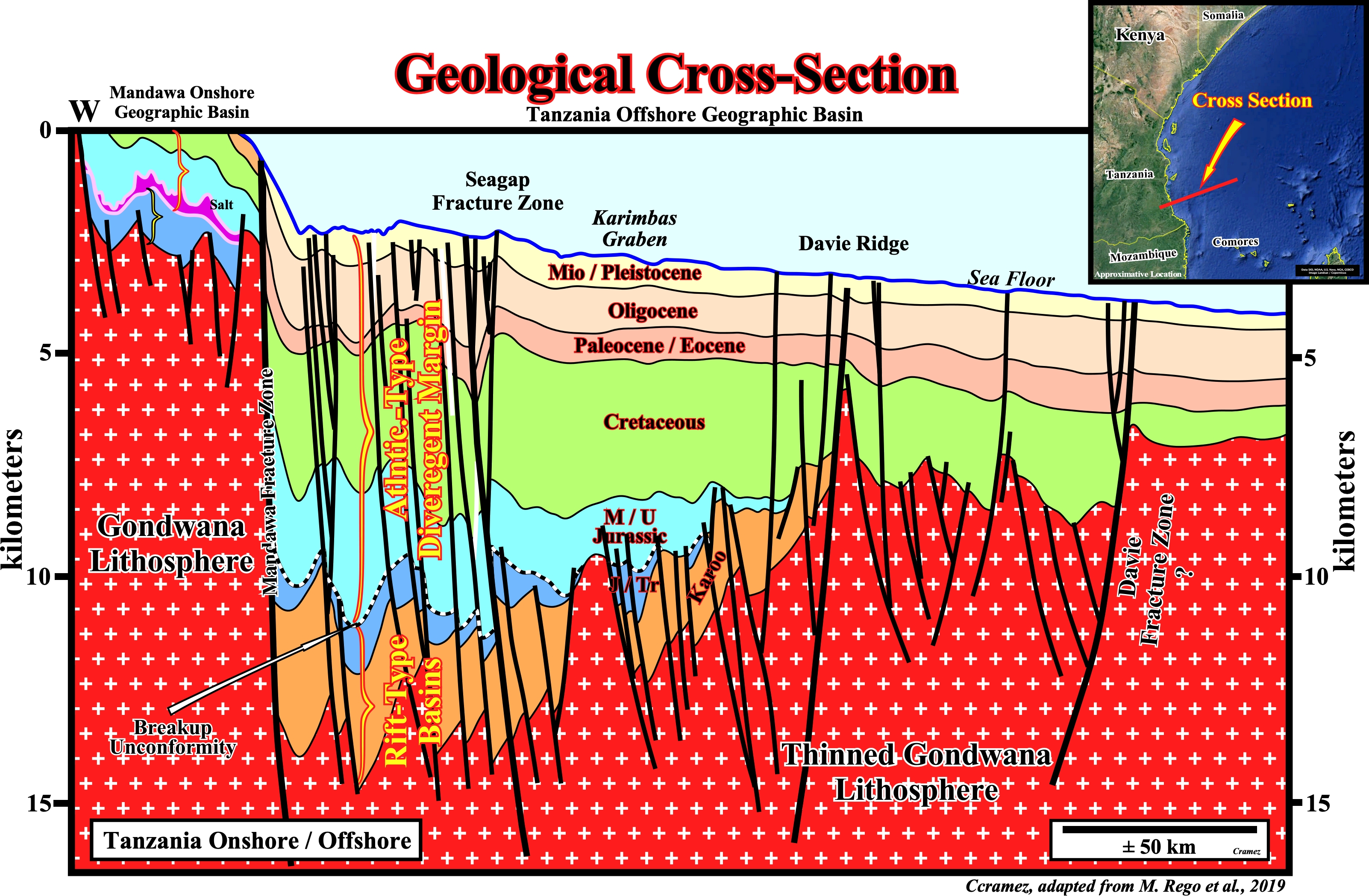
On this West-East geological cross-section of the southern Tanzania through the Mandawa onshore geographic basin and the adjacent offshore several major fracture zones are, easily, recognized : (i) Mandawa Fracture zone, (ii) Seagap Fracture Zone ; (iii) Davie ridge and the Davie Fracture Zone. The Mandawa fracture zone limits, roughly, the onshore from the offshore. It is, probably, the main responsible for the abrupt water depth change between the onshore and offshore environments. In fact, presently, the basin has not shelf, i.e., the shoreline corresponds, practically, to the shelf break. The Seagap fracture zone seems to have a compressional strike-slip movement. Not only the sedimentary packages are, laterally, displaced but those of the eastern faulted are, slightly, shortened as well. The Davie Ridge is, probably, the northward continuation of the subduction zone hypothesized on Mozambique offshore (see Page 35 and 36B). It marks the eastern limit of the Karoo sediments, that is to say, non-marine sediments (shales, red beds, siltstones) and great quantities of volcanics, extending from the Carboniferous and Permian periods to the Late Triassic Epoch. The Davie fracture zone, which is eastern fracture zone of the area, seems to have played with an extensional strike-slip movement, mainly, during the Atlantic-type divergent margin (Cretaceous time). Stratigraphically, the pre-breakup rift-type basins are, easily, recognized. They have a Karroo and Early Jurassic age. The Atlantic-type divergent margin is quite well developed with an important thermal subsidence during the Jurassic and Cretaceous, while during the Tertiary the sedimentary packages are roughly isopachous. In other words, during the Jurassic and Cretaceous the major factor in the creation of the space available for sediments was the subsidence, while during the Tertiary, eustasy was paramount. Notice, in the onshore, the presence a salt deposits at the base of the Atlantic-type margin (Kizimbani-1 well, recognized 750 m of evaporites , which according certain geoscientists seem to emplaced between Bathonian and Late Aptian strata (Balduzzi et al., 1992).
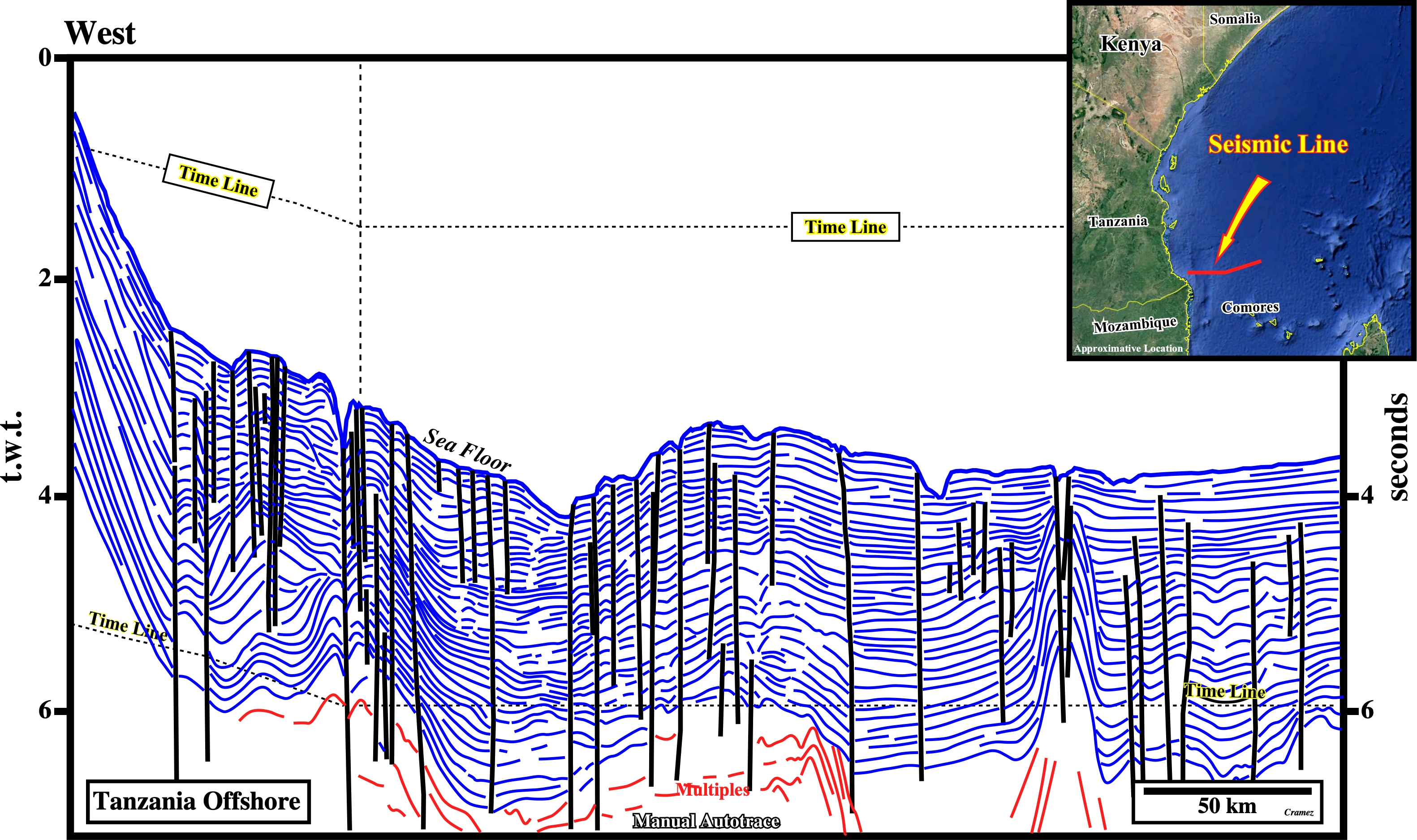
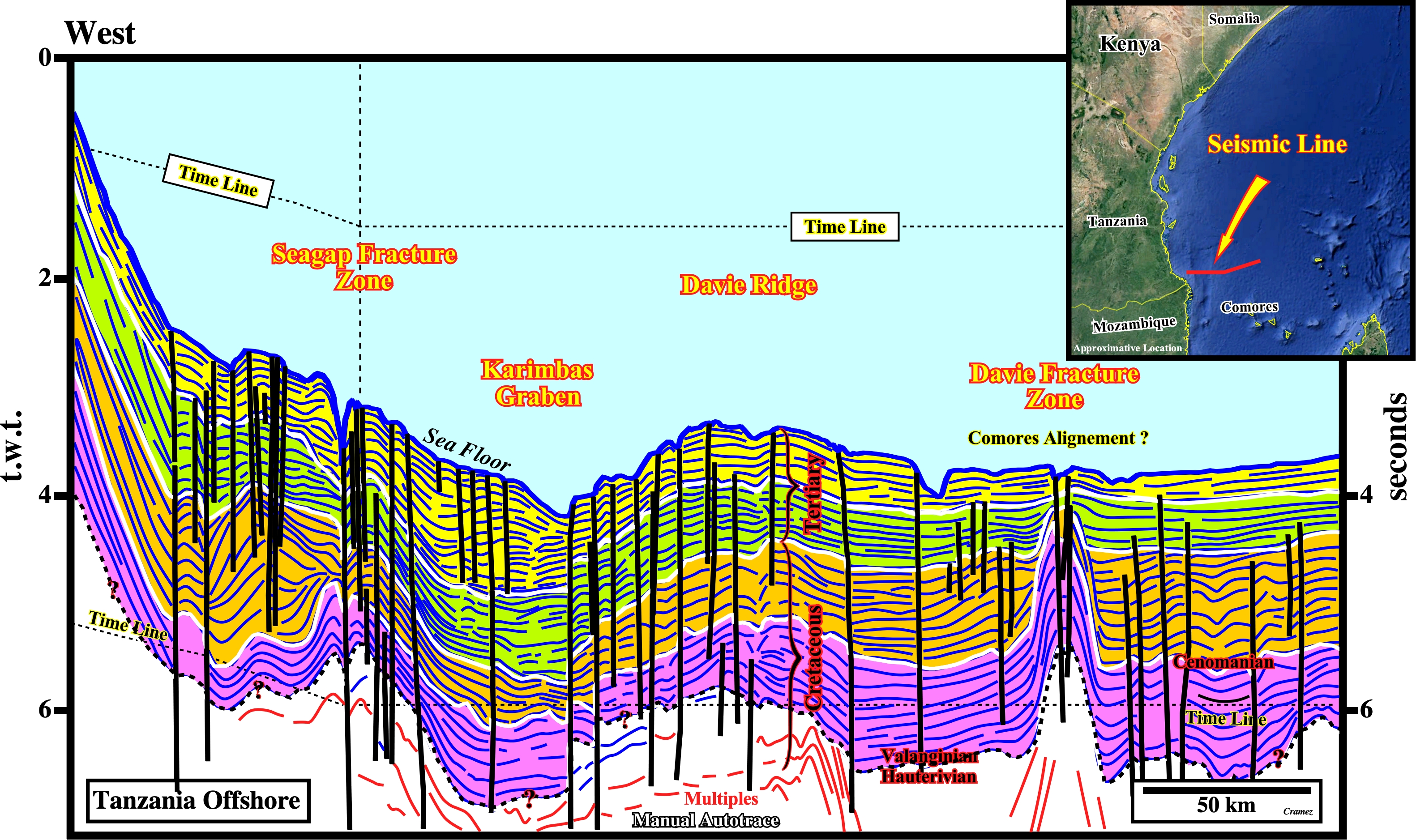
On this manual autotrace of an old unmigrated composite seismic line (too much multiples and diffractions) of Tanzania offshore seismic line, located northward of the offshore Rovuma geographic basin ( Mozambique) and southward of the geological cross-section illustrated on the previous plate, the Seagap Fracture Zone, the Karimbas Graben, the Davie Ridge and the Davie Fracture Zone (?) are quite well recognized. It is important to notice that in this area, the Tertiary gravitary folded belt of the Rovuma geographic basin (Mozambique offshore, see Page 36A) is, totally, absent. Similarly, the Lacerda graben (see Page 41) did not reach this area. At the stratigraphic point of view, just the upper part of the Atlantic-type divergent margin is recognized. Below the Lower Cretaceous sediments (Neocomian, i.e., Valanginian and Hauterivian), the data is very poor and the majority of the seismic reflection are multiples and diffractions.
Send E-mails to carlos.cramez@bluewin.ch with comments and suggestions to improve this atlas.
Copyright © 2001 CCramez
Last update:
2022