

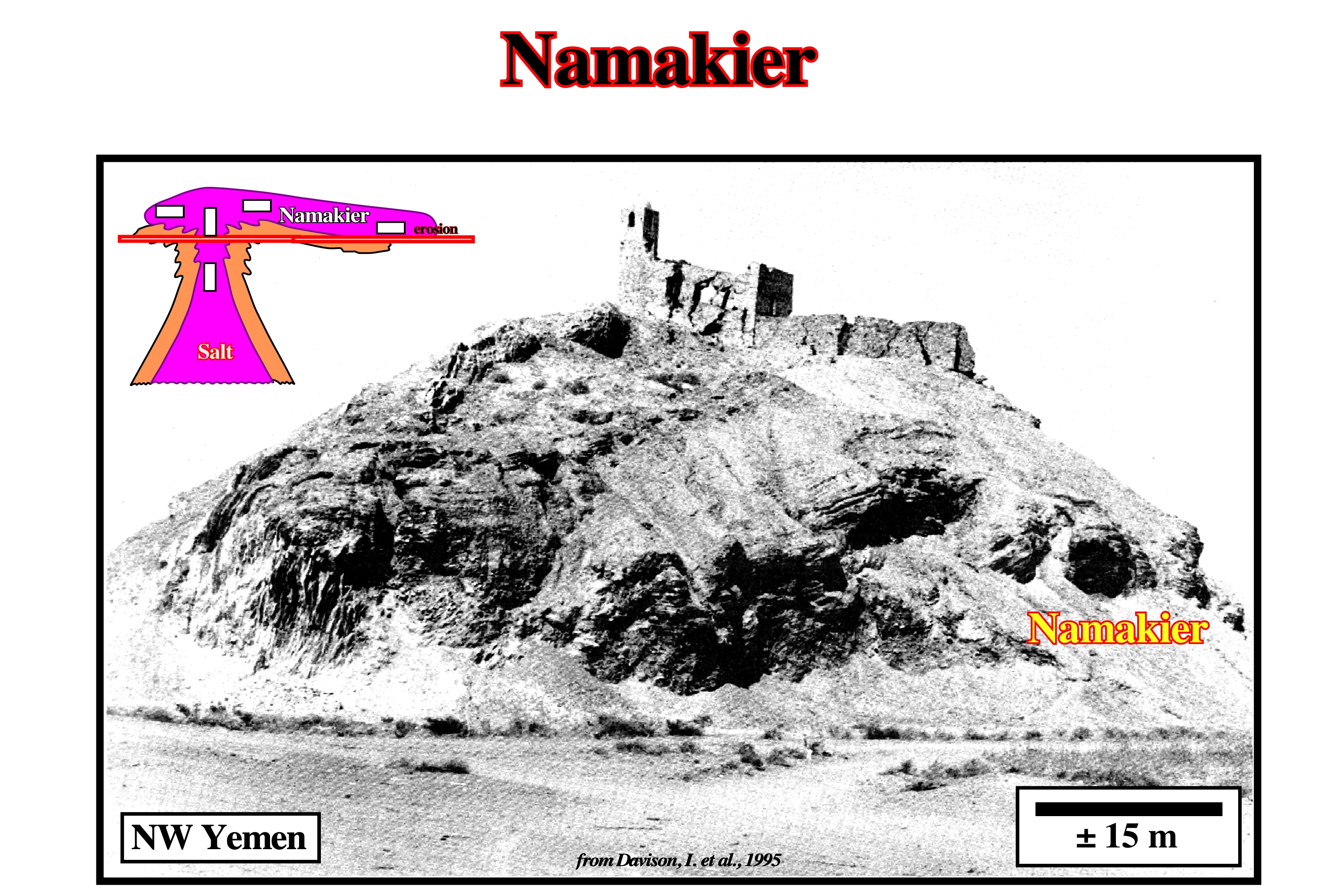
Namakier
Synonym of Salt Glacier.
Photograph of the NE flank of the Jabal Al Milh (NE Yemen) salt diapir, where the bedding is overturned, folding and thrusted and later gravity-driven extension has cracked the 80-100 year old mosque walls.
Nitrates (Bates, R. L. and Jackson, J. A., 1980)
Minerals characterized by a fundamental anionic structure of NO3. Examples of nitrates are: NaNO3 (soda niter) and KNO3(niter).
The whole life form requires nitrogen compounds (proteins and nucleic acids). The air has about 80% nitrogen (N2 ) and is the largest nitrogen reservoir. Most organisms can not use nitrogen directly. Plants use nitrogen by incorporating certain compounds, such as: (i) nitrate ions (NO3-) ; (ii) Ammonia (NH3) ; (iii) Urea (NH2)2CO, etc. The animals use the nitrogen compounds by eating the plants. In the biosphere, four processes participate in the nitrogen cycle: (a) Fixation ; (b) Denitrification ; (c) Nitrification and (d) Assimilation. In fixation, three processes are responsible for the majority of nitrogen fixation in the biosphere: 1) Atmospheric Fixation by Light ; 2) Biological Fixation (microbes) and 3) Industrial Fixation. Denitrification is a chemical-biological process of formation of nitrite in the soil by the joint action of nitrifying chemosynthesizing bacteria, by the conversion of ammonia into nitrate, which occurs in two stages: (A) Nitrification, 2NH3 (ammonia) + 3O2 → 3O2 → 2H+ + 2NO2- (nitrite) + 2H2O + energy and (B) Nitrification, 2NO2-(nitrite) +O2 → 2NO3-(nitrate) + energy. Nitrification is a biological oxidation of ammonia to nitrate with the formation of nitrite as an intermediate under aerobic conditions. The conversion to nitrites (2NH4 + 3O2→NO2- + 4H+ +2H2O) and nitrates (2NO2- + O2 →2NO3-) involves two species of specific autotrophic bacteria, respectively Nitrosomone and Nitrobacter that obtain energy from inorganic compounds as ammonia and nitrites .In the assimilation, the proteins made by the plants enter the food chains and their metabolism produces organic compounds of nitrogen that return to the environment, mainly, in the form of excretions and that under the action of certain micro-organisms produce ammonia. In nitrification, the ammonia can be directly incorporated by the plants through the roots. However, much of the ammonia produced by decomposition is converted into nitrates, which is done in two steps: bacteria of the genus Nitrosomone oxidize NHO3 to NO2- and bacteria of the genus Nitrobacter oxidize nitrites (NO2-) to nitrates. The three preceding processes draw nitrogen from the atmosphere and incorporate it into ecosystems. Denitrification reduces nitrates into nitrogen (gas) which replaces nitrogen in the atmosphere. Bacteria are the major agents, since they use nitrates as an alternative to oxygen for their respiration.
Non-uniform Flow
Flow with nonparallel streamlines. Converging streamlines represent accelerating flows. Diverging streamlines represent decelerating flows.
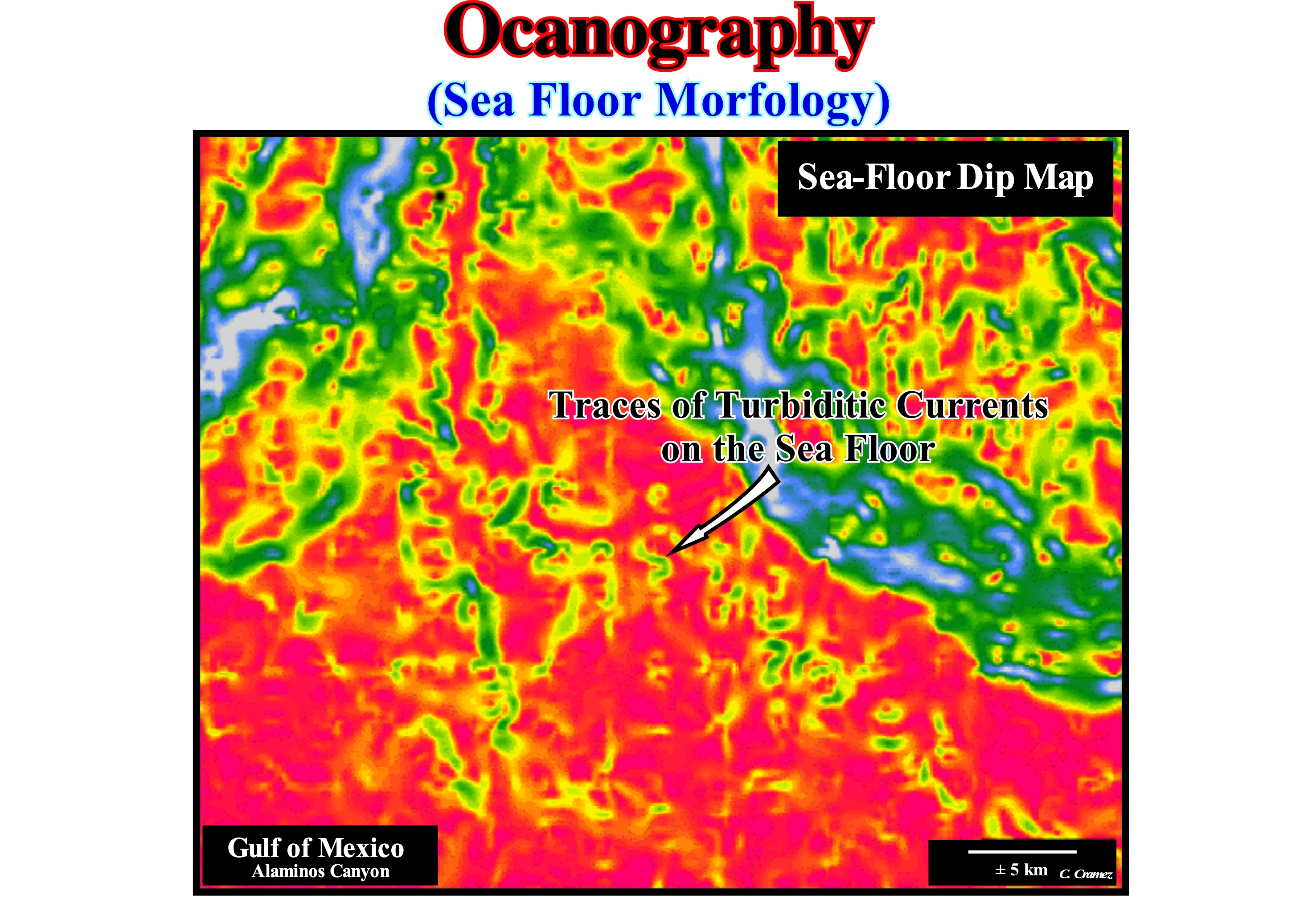
Flow is said to be non-uniform, when there is a change in velocity of the flow at different points in a flowing fluid, for a given time. For instance, the flow of liquids under pressure through long pipelines of varying diameter is referred to as non-uniform flow. Streamlines are used for visualizing the flow. Several streamlines make up a flow pattern. A streamline is a line drawn through the flow field such that the flow vector is tangent to it at every point at a given instant in time. Using "S" as the spatial variable along the path (i.e., along a streamline), the flow is uniform when δv / δs is equal to zero.
Normal Stress
Stress acting normal to a plane. A normal stress is symbolized by Greek letter σ (sigma).
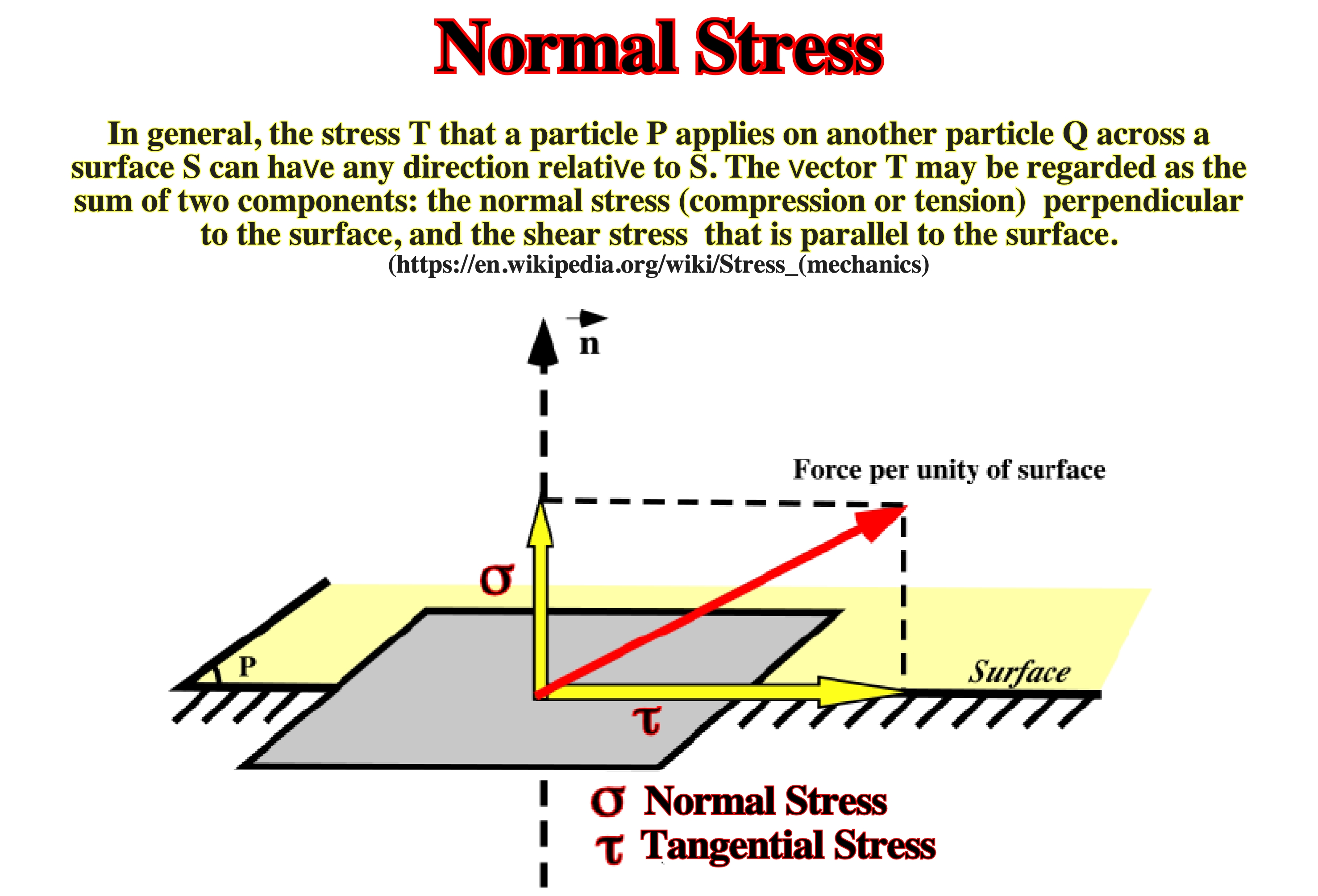
Normal stresses can be: (i) Compressional or positive, depicted by convergent arrows or by a symbol plus and (ii) Tensional or negative, represented by two arrows in opposite directions or by the symbol minus.