
Universidade Fernando Pessoa
Porto, Portugal

Seismic-Sequential Stratigraphy
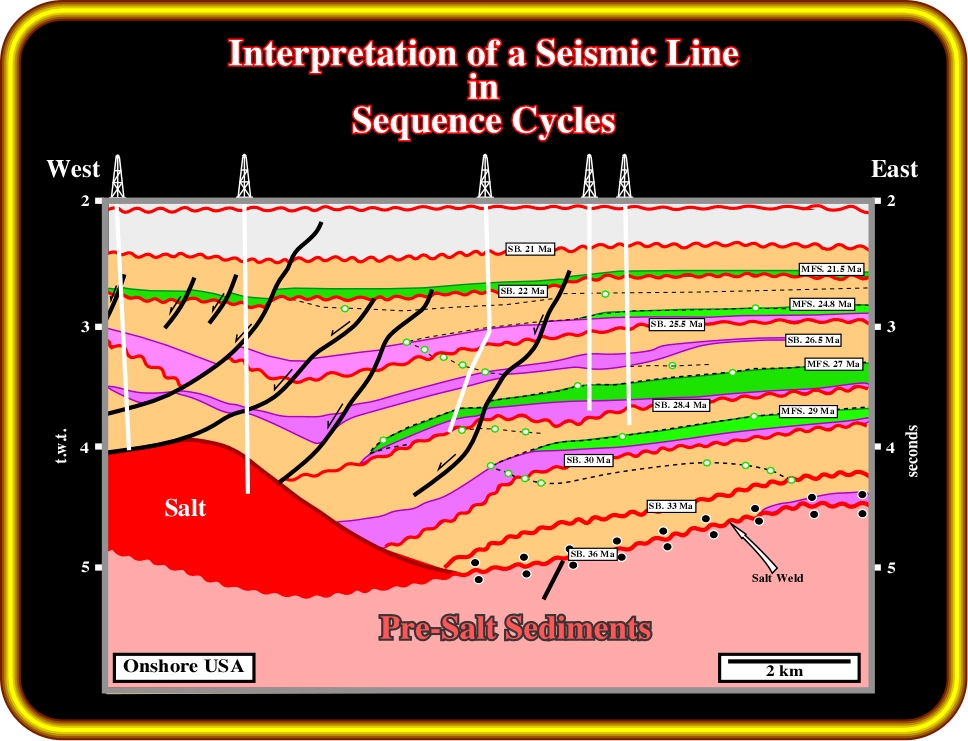
This interpretation of a seismic line of the onshore USA was performed at a high hierarchic level (sequence-cycles). The post-salt interval was interpreted in stratigraphic sequence-cycles, which are deposited during 3rd eustatic cycles. Each of these cycles is bounded by unconformities. The time-interval between the lower and upper unconformities ranges between 0.5 and 3-5 My. Such a time-interval should not be confounded with the total time-deposition of the sediments composing a sequence-cycle (the completeness of the different systems tracts making up a sequence-cycle is rarely 1). From bottom to top, each sequence-cycle, when complete, is composed by (i) a Lowstand systems tract (LST), in purple on the interpretation, (ii) a Transgressive systems tract (TST), in green, and (iii) Highstand systems tract (HST), in orange. Three members can be often subdivided into Lowstand systems tract (LST): 1- Basin floor fan (BFF) at the bottom, 2- Slope fan (SF) in the middle and 3-Lowstand prograding wedge (LPW) at the top. A systems tract is a lateral linkage of contemporaneous and genetically related depositional systems. Do not forget that, by conventional My (millions years) means an internal of time, while Ma, as for instance SB. 30 Ma, is an age, in this particular case the age of a stratigraphic cycle boundary. If we have problems understanding these comments you really need to spend few minutes taking a look at the next webpages.
Contents:
Introduction
A) Geophysical Surveying
B) Potential Methods
B.1) Magnetism
B.2) Gravimetry
C) Seismic Exploration Basic Review
D) Seismic Reflection Basics
E) Interpretation Difficulties
E.1) Time Sections versus Depth Sections
E.2) Unmigrated versus Migrated Profiles
E.3) Lateral arrivals
E.4) Multiples
E.5) Diffractions
E.6) Reflected Refractions
E.7) Static Corrections
F) Geological Models and Seismic Responses
F.1) Monoclines
F.2) Normal Faults
F.3) Reverse Faults
F.4) Shale Domes
F.5) Salt Domes
F.6) Reefs
F.7) Canyons
F.8) Freezing
F.9) Synforms
Driving Concepts
1) Time Stratigraphy
2) Time Line in Rocks
3) Systems Tracts & Facies
Depositional Model
Stratigraphic Concepts
Stratigraphic Boundaries
Geometrical Relationships
1) Onlap
2) Downlap
3) Toplap
4) Truncation
Discontinuity Surfaces
a) Unconformities
b) Depositional Hiatus
External Forms & Internal Configurations
1) Filling Patterns
2) Progradational Patterns
Significance of Geometrical Configurations
Diachronous Surfaces
Sequential Stratigraphy
Sequential Stratigraphy Analysis
Sequential versus Genetical Stratigraphy
Hierarchical Level of Interpretation
Controlling Parameters of Sequential Stratigraphy
A) Eustasy or Eustatism
A.1- Eustasy Metaphor
A.2- Geoid
A.3- Geoid Changes
B) Eustatic Cycles
C) Climate (Glaciations)
C.1- Origin of the Ice Ages
D) Subsidence & Accommodation
E) Terrigeneous Influx
Tectonic versus Eustasy
Eustatic and Stratigraphic Cycles
a) Continental Encroachment Cycle
b) Continental Encroachment Sub-cycle
c) Sequence Cycle
d) Parasequence Cycle
Depositional Models
Marco Polo Software
1) Sand-Shale Model
1.1) Evolution of the Sand-Shale Model
1.2) Model Variables Impact
2) Carbonate Model
Exercises
a) Depositional Costal Break
b) Paleowater Depth
c) Accommodation
d) Bayline
Systems Tracts
1) Lowstand Systems Tract (LST)
a) Geological Settings
a.1- Deepwater Setting
a.2- Ramp Setting
a.3-Growth Fault Setting
b) Lower Member: Basin Floor Fan (BFF)
c) Middle Member: Slope Fan (SF)
d) Upper Member: Lowstand Prograding Wedge (LPW)
e) Turbidite Deposits Associated with LPW
f) Submarine Canyon Fill (SCF) & Incised Valley fill (IVF)
2) Transgressive Systems Tract (TST)
3) Highstand Systems Tract (HST)
4) Neogene Global Stratigraphic Signature
5) Recapitulation
5.1- Sequence Cycle Model
- Systems Tracts
- Relative Sea Level
5.2- Sea Level Responses to Orbital Perturbations and Subsidence
5.3- Major Transgressive - Regressive Cycles
5.4- Availabl Space & Sediment Supply
5.5- Paleobathymetry, Faunal Peaks, Depositional Systems, Lithofacies, Electric Log Patterns, Dipmeter, Systems Tracts, Color Code
5.6- Sea Level and Systems Tracts
6) Meso - Cenozoic Cycle Chart
7) Bibliography